
GN-A kit

GN-B kit
Identifies the complete range of Enterobacteriaceae and other non-fastidious, oxidase positive and negative, gram negative bacilli. The GN-A kit includes 60 microwell strips in foil pouches, frame for microwell strips, result forms, instructions for use and color chart for reading results. GN-A kit can be used separately from GN-B kit. GN-B kit includes 24 microwell strips in foil pouches and instructions for use. GN-B kit is designed to be used together with GN-A kit and not on its own. Identification software and reagents must be purchased separately.

Features list
- Simple to inoculate, handle and read
- Strip includes all tests in ISO and other standard methods
- No toxic reagents
- Results within 24 hours
- 100% sensitivity
- No MacFarland calibration
- Ability to isolate directly from chromogenic media
- No need for additional tests
- No assembly required
- No weak color changes
- Cost efficient
Easy to use:
- Select a single colony of the isolate to be identified
- Emulsify colony in 3ml saline (A) or 5ml saline (A+B
- Add 3-4 drops (100µL) of the suspension to each well of the strip(s)
- Overlay appropriate wells with mineral oil
- Incubate 18-24 hours at 35-37°C
- Next day add reagents
- Read and Record results using the color chart (provided) and Identification Software (purchased separately)
The GN-ID system comprises two separate, 12-substrate, microwell strips; the GN-A microwell strip and the GN-B microwell strip. The GN-A strip can be used separately and identifies the most commonly encountered, oxidase negative, non-fastidious, gram negative bacilli. GN-B is designed to be used in conjunction with GN-A; the combined strips identify the complete range of Enterobacteriaceae and other non-fastidious, oxidase positive and negative, gram negative bacilli. The wells in each microwell strip contain dehydrated biochemical substrates that are reconstituted with a saline suspension of the organism to be identified. If the substrate found in each well is metabolized by the organism, then a color change occurs during incubation or after the addition of specific reagents. Substrates are based on conventional biochemical methods used for identifying Enterobacteriaceae and other gram negative bacilli.
Procedure
A pure, 18-24 hour culture of the isolate to be identified must always be used. We suggest selecting a single colony from EZ-CHROM chromogenic media. An oxidase test must be performed on the isolate prior to strip inoculation. Oxidase positive organisms can only be identified when A and B strips are both inoculated. Emulsify a single colony from an 18-24 hour culture in sterile physiological saline (3 ml for strip A, 3-5 mls for A+B). Mix thoroughly. Add 3-4 drops (100µL) of the suspension to each well of the strip(s). After inoculation, overlay specified wells with 3-4 drops of mineral oil; these wells are highlighted with a black circle around the well to assist in adding oil to the correct wells. Seal the top of the microwell strip(s) with adhesive strip provided and incubate at 35-37oC for 18-24 hours. Remove adhesive strip and record all positive reaction with the aid of the color chart. Add Indole Kovacs, VP I & II, Nitrate A & B and TDA reagents to the appropriate wells as described in the Instructions for Use. Read and record results using the color chart and Identification Software (sold separately). For a complete explanation of procedure for use, please refer to the Instructions for Use, included with your kit.

Step 1: Select a single colony

Step 2: Emulsify in saline solution
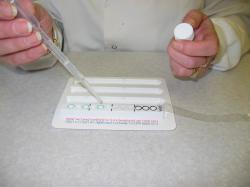
Step 3: Inoculate strip with solution

Step 4: Add mineral oil

Step 5: Apply adhesive strip and incubate

Step 6: Next day, add reagents

Step 7: Read and record results
The Microgen™ GN-A will identify the following:
- Acinetobacter spp.
- baumannii
- lwoffi
- A .haemolyticus
- Citrobacter spp.
- freundii
- diversus
- Enterobacter spp.
- aerogenes
- cloacae
- agglomerans
- E. gergoviae
- E. sakazakii
- Escherichia spp.
- E. coli
- E. coli-inactive
- E. vulneris
- Shigella spp.
- S. dysenteriae (Group A)
- S. flexneri (Group B)
- S. boydii (Group C)
- S. sonnei (Group D)
- Hafnia spp.
- alvei
- Klebsiella spp.
- K. pneumoniae
- K. oxytoca
- K. ozaenae
- K. rhinoscleromatis
- Morganella spp.
- M. morganii
- Proteus spp.
- P. mirabiliis
- P. vulneris
- Providencia spp.
- P. rettgeri
- P. stuartii
- P. alcalifaciens
- Salmonella spp.
- Salmonella Group I
- S. Typhi
- S. Cholerae-suis
- S. Paratyphi A
- Salmonella Group II
- Salmonella Group IIIa
- Salmonella Group IIIb
- Salmonella Group IV
- Salmonella Group V
- Salmonella Group VI
- Serratia spp.
- S. marcescens
- S. liquefaciens
- S. rubidaea
- Tatumella spp.
- T. ptyseos
- Yersinia spp.
- Y. enterocolitica
- Y. pseudotuberculosis
Species identified using the Microgen™ GN A + B Panel (OXIDASE NEGATIVE)
- Acinetobacter spp.
- baumannii
- lwoffi
- haemolyticus
- Budvicia spp.
- aquatica
- Buttiauxella spp.
- agrestis
- brennerae
- ferragutiae
- gaviniae
- B .izardi
- noackiae
- wamboldiae
- Cedecea spp.
- davisae
- lapagei
- neteri
- Cedecea sp 3
- Cedecea sp 5
- Citrobacter spp.
- freundii
- diversus
- C. amalonaticus
- C. farmeri
- C. youngae
- C. braakii
- C. werkmanii
- C. sedlakii
- C. rodentium
- Citrobacter sp 10
- Citrobacter sp11
- Edwardsiella spp.
- tarda
- tarda biogp1
- hoshinae
- ictaluri
- Enterobacter spp.
- aerogenes
- cloacae
- agglomerans
- gergoviae
- E. sakazakii
- E. taylorae (cancerogenus)
- E. amnigensis biogp1
- E. amnigensis biogp2
- E. asburiae
- E. hormaechei
- E. intermedium
- E. cancerogenus
- E. dissolvens
- E. nimipressuralis
- E. pyrinus
- Escherichia spp.
- E. coli
- E. coli-inactive (previously Alkalescens-Dispar Group)
- E. fergusonii
- E. hermannii
- E. vulneris
- E. blattae
- Shigella spp.
- S. dysenteriae (Group A)
- S. flexneri (Group B)
- S. boydii (Group C)
- S. sonnei (Group D)
- Ewingella spp.
- E. americana
- Hafnia spp.
- alvei
- alvei biogp1
- Klebsiella spp.
- K. pneumoniae
- K. oxytoca
- K. ornithinolytica
- K. planticola
- K. ozaenae
- K. rhinoscleromatis
- K. terrigena
- Kluyvera spp.
- K. ascorbata
- K. cryocrescens
- K. georgiana
- K. cochlea
- Leclercia spp.
- L. adecarboxylata
- Leminorella spp
- L.grimontii
- L.richardii
- Moellerella spp.
- M. wisconsensis
- Morganella spp.
- M. morganii
- M. morganii subsp morganii
- M. morganii biogp1
- M. morganii subsp siboni 1
- Obesumbacterium spp.
- O. proteus biogp2
- Pragia spp.
- P. fontium
- Pantoea spp.
- P. dispersa
- Photorhabdus spp.
- P. luminescens (25°C)
- Photorhabdus DNA Group 5
- Proteus spp.
- P. mirabilis
- P. vulgaris
- P. penneri
- P. myxofaciens
- Providencia spp.
- P. rettgeri
- P. stuartii
- P. alcalifaciens
- P. rustigianii
- P. heimbachae
- Rahnella spp.
- R. aquatilis
- Salmonella spp.
- Salmonella Group I
- S. Typhi
- S. Cholerae-suis
- S. Paratyphi A
- S. Gallinarum
- S. Pullorum
- Salmonella Group II
- Salmonella Group IIIa
- Salmonella Group IIIb
- Salmonella Group IV
- Salmonella Group V
- Salmonella Group VI
- Serratia spp.
- S. marcescens
- S. marcescens biogp1
- S. liquefaciens
- S. rubidaea
- S. odorifera biogp1
- S. odorifera biogp2
- S. plymuthica
- S. ficaria
- S. entomophila
- S. fonticola
- Tatumella spp.
- T. ptyeos
- Trabulsiella spp.
- T. guamensis
- Xenorhabdus spp.
- X. nematophilis (25°C)
- Xanthomonas spp.
- X.(S) maltophilia
- Yersinia spp.
- Y. enterocolitica
- Y. frederiksenii
- Y. intermedia
- Y. kristensenii
- Y. rohdei
- Y. aldovae
- Y. bercovieri
- Y. mollaretii
- Y. pestis
- Y. pseudotuberculosis
- Y. ruckeri
- Yokenella spp.
- Y. regensburgei
- Enteric gp58
- Enteric gp59
- Enteric gp60
- Enteric gp63
- Enteric gp64
- Enteric gp68
- Enteric gp69
Species identified using the Microgen™ GN A + B Panel (OXIDASE POSITIVE)
- Actinobacillus spp.
- Aeromonas spp.
- hydrophila
- veronii bio sobria
- veronii bio veronii
- caviae
- Alcaligenes spp.
- faecalis type 11
- faecalis
- xylosoxidans subsp xylos
- Burkholderia spp.
- cepacia
- pseudomallei
- Flavobacterium spp.
- F. meningosepticum
- F. odoratum
- F. breve
- F. indologenes
- Moraxella spp.
- Pasteurella spp.
- P. multocida
- P. haemolytica
- Plesiomonas spp.
- P. shigelloides
- Pseudomonas spp.
- Ps. aeruginosa
- Ps. fluorescens-25°C
- Ps. fluorescens-37°C
- Ps. putida
- Ps. stutzeri
- Ps. diminuta
- Shewanella spp.
- S. putrefaciens
- Vibrio spp.
- V. fluvialis
- V. furnissii
- V. mimicus
- V. vulnificus
- V. hollisae
- V. choleras
- V. parahaemolyticus
- V. alginolyticus
- V. cincinnatiensis
- V. damsela
- V. carchariae
- Weeksella spp.
- W. virosa
- W. zoohelcum
| Gram Negative (GN) ID | |
| Storage |
The microwell strips are stable in the unopened foil pouches at 2-8oC until the expiry date stated. Once the foil pouch has been opened, unused microwell strips should be replaced into the pouch and the pouch resealed. Microwell strips in resealed pouches should be used within 14 days. |
| Shelf Life | 1 year |
| Well Substrates | |
| GN-A Strip |
Well 1- Lysine Well 2- Ornithine Well 3- H2S Well 4- Gluclose Well 5- Mannitol Well 6- Xylose Well 7- ONPG Well 8- Indole Well 9- Urease Well 10- VP Well 11- Citrate Well 12- TDA |
| GN-B Strip |
Well 13- Gelatin Well 14- Malonate Well 15- Inositol Well 16- Sorbitol Well 17- Rhamnose Well 18- Sucrose Well 19- Lactose Well 20- Arabinose Well 21- Adonitol Well 22- Raffinose Well 23- Salicin Well 24- Arginine |
| Reagents |
Indole Kovacs TDA Voges-Proskauer I Voges-Proskauer II Nitrate Reagent A Nitrate Reagent B Mineral Oil |


